Buy TDS Meter @ Best Price Online – Accurate Water Quality Testing Device
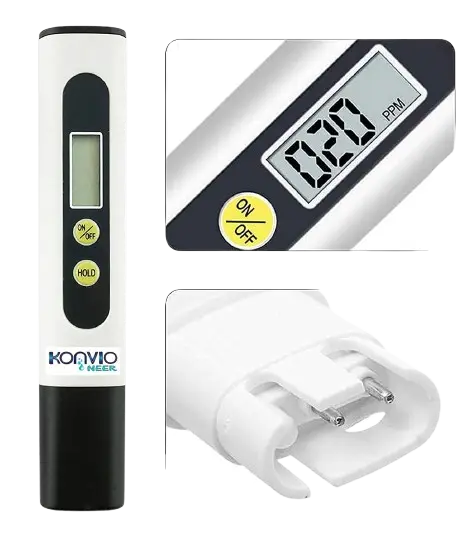
Imported Tds Meter, Total Dissolved Solids Meter, Water Quality Tester, Ppm Tester For Water Testing – White
Pure, safe water is vital for every home—but how can you be sure the water you drink is genuinely free from risks? The answer is simple – use a TDS Meter.
A T.D.S Meter is a handy digital water testing device that helps you measure the Total Dissolved Solids in your drinking water. Whether it’s for your home, office, aquarium, or RO purifier, a TDS Meter gives you quick and accurate results.
If you’re searching for the best TDS Meter price to buy online, you’re in the right place. We offer high-quality T.D.S Meters that are affordable, easy-to-use, and reliable for everyday water testing.
Top 10 Best Water Purifier in India – 2025 / Expert Review
What is a TDS Meter?
A T.D.S Meter is a compact digital device designed to check the level of dissolved solids in water. These solids include minerals, salts, and impurities. The reading is displayed in parts per million (ppm), which shows whether your water is safe for drinking or needs purification.
-
- For Home & RO Systems – A T.D.S Meter ensures your purifier is delivering safe water.
-
- For Aquariums – Use a T.D.S Meter to maintain the correct mineral balance for fish and aquatic plants.
-
- For Borewell or Tank Water – A T.D.S Meter helps identify impurities and excess hardness.
-
- For Labs & Commercial Use – A T.D.S Meter is essential for hydroponics, beverages, and industrial water testing.

“Buy Aqua Copper Water Purifier 12 Ltr @ Best Price”
Benefits of Using a TDS Meter





How to Use a TDS Meter?

Buy Imported Tds Meter, Total Dissolved Solids Meter, Water Quality Tester, Ppm Tester For Water Testing – White
Using a T.D.S Meter is very simple:
-
- Switch on the T.D.S Meter.
-
- Dip the sensor into the water sample.
-
- Wait a few seconds until the reading stabilizes.
-
- Check the T.D.S level in ppm.

Why Buy TDS Meter Online from Us?
When you choose to buy T.D.S Meter online, you want accuracy, quality, and affordability. That’s exactly what we provide.
-
100% genuine T.D.S Meters with warranty
-
Best prices across India
-
Easy online ordering and fast delivery
-
Professional tips to select the most suitable T.D.S Meter
-
Trusted by thousands of happy customers
Best TDS Meter Price in India
The T.D.S Meter price is very affordable, making it a smart investment for health-conscious families.
-
- Basic T.D.S Meters – Perfect for home and RO systems.
-
- Advanced Digital T.D.S Meters – With auto temperature compensation.
-
- Multi-Parameter Devices – Measure T.D.S, pH, EC, and temperature in one tool.

Shop TDS Meter Online – Quick & Secure
Buying a T.D.S Meter online is fast and hassle-free. Simply browse, compare, and order with a few clicks. We offer:
-
Secure online payment options
-
Cash on Delivery (COD) available
-
Nationwide fast delivery
Whether you live in Bangalore, Delhi, Mumbai, or anywhere in India, your T.D.S Meter will reach your doorstep quickly.
You Can Also Check Water Purifier Model and Prices
Aquaguard Water Purifier
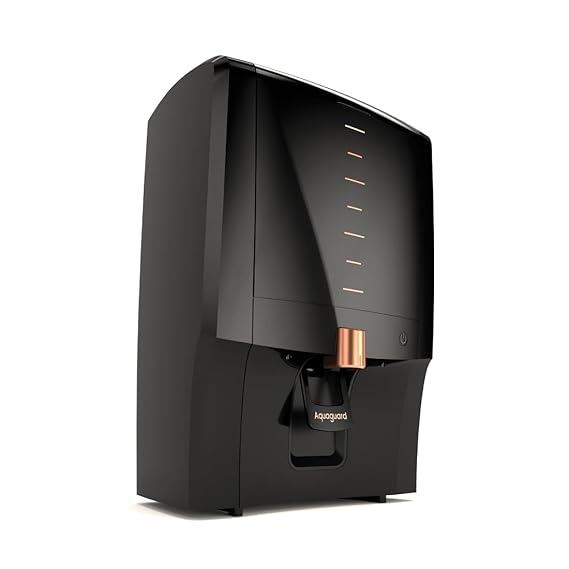

Buy Aquaguard Water Purifier Enrich Aura 2X Aquasaver RO+UV+Copper | Needs No Service for 2 Years | 60% Water Saving | Includes Mega Sediment filter | 7-Stage Purification | 7L storage
Livpure Water Purifier

Livpure GLO PRO++ RO+UV+UF | Free Service For 2 Years | Filters Included | 7 L Storage | Suitable for Borewell, Tanker, Municipal Water | 2 Year Warranty | Black
Kent Water Purifier
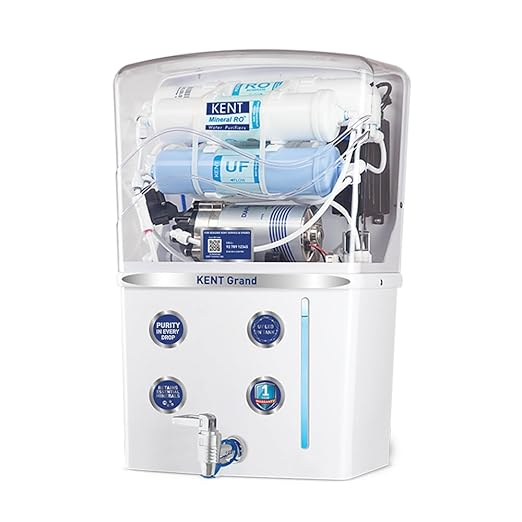

KENT Grand RO Water Purifier | Advanced RO Tech for Sabse Shudh Paani | RO+UF+TDS Control + UV LED Tank | 8L | 20LPH Flow | Ideal for Borewell/Tanker/Municipal Water | Largest Service Network
Urban Company M1 Water Purifier
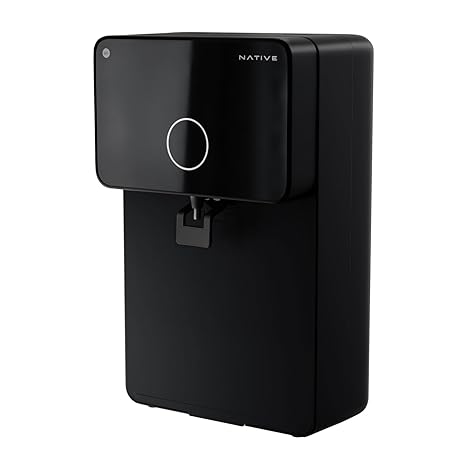

Native by UC Urban Company M1 Water Purifier | Needs No Service For 2 Years | RO+UV+Copper+Alkaline | 10-Stage Purifier | 4-in-1 Health Booster | 8L Capacity | 2 Year Warranty (Filters Included)

How to Select a Water Purifier
Access to safe drinking water is one of the most important needs for every household. Unfortunately, tap water today often contains impurities, harmful chemicals, or disease-causing microorganisms. That’s why investing in a good water purifier has become essential. But with so many brands and technologies available, how do you decide which one is right for your family? Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you select the perfect water purifier.
1. Understand Your Water Quality
The first and most important step is to check the type of water that comes into your home. Check the TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) level and look for contamination in the water.
-
- If the TDS is high (above 500 ppm), your water likely contains excess salts and hardness, which requires an RO purifier.
-
- If the TDS is low but you’re worried about germs, a UV purifier works well.
-
- If you mainly deal with muddy or cloudy water, choose a purifier with UF or sediment filters.
Knowing your water quality ensures you don’t overspend on unnecessary features.
2. Pick the Right Technology
Modern purifiers use different purification methods:
-
- RO (Reverse Osmosis): Best for hard water and high TDS; removes salts, fluoride, and heavy metals.
-
- UV (Ultraviolet): Eliminates bacteria and viruses, ideal for soft water with microbial impurities.
-
- UF (Ultrafiltration): Works without electricity; blocks dirt and germs but not dissolved salts.
-
- RO + UV + UF with Copper/Alkaline: Advanced purifiers combine multiple technologies to provide safe, tasty, and mineral-balanced water.
Choose a model that matches your exact water condition.
3. Check Storage Capacity
If your area has power cuts or irregular supply, buy a purifier with 7–10 liters of storage. Smaller families in cities with 24/7 water supply can manage with 5–7 liters. Storage is a practical factor often overlooked during purchase.
4. Look at Maintenance & Service
Every purifier needs filter replacements and servicing. Before buying, ask about annual maintenance charges (AMC) and ensure that service centers are available in your city. A reliable brand with easy access to spare parts will save you both money and hassle in the long run.
5. Explore Extra Features
Today’s purifiers are designed with more than just basic filtration. Some added features to consider are:
-
- Copper-infused water for natural immunity.
-
- Alkaline filters to maintain the body’s pH balance.
-
- Filter-change alerts so you never forget maintenance.
-
- Energy-saving designs for cost efficiency.
6. Budget and Warranty
Prices vary depending on features. A quality RO + UV + UF purifier usually ranges between ₹7,000 and ₹15,000. Always check for a 1–2 year warranty and good after-sales service before finalizing your purchase.
Conclusion
Choosing the right water purifier is not about picking the most expensive model—it’s about selecting one that fits your water type, family size, and budget. By testing your water, understanding purification technologies, and considering storage and maintenance, you can make a smart investment. The right purifier will ensure clean, safe, and great-tasting water for your family every day.
Buy TDS Meter online at the best price in India with fast delivery.
Shop digital TDS Meter for water testing online at affordable prices.
Best TDS Meter for RO water purifier – order online now.
Buy pocket TDS Meter for home, office, and aquarium use.
Get accurate digital TDS Meter online with warranty.
Compare TDS Meter prices online and choose the best deal.
Buy water quality testing TDS Meter online for drinking water.
Best budget TDS Meter for household and industrial use.
Order TDS Meter for aquarium and hydroponics online.
Buy professional TDS Meter with temperature sensor online.
High accuracy TDS Meter for RO water purifier at low price.
Shop portable TDS Meter online for quick water testing.
Get the best digital TDS Meter under ₹500 online in India.
Buy TDS Meter kit online for water hardness and purity check.
Trusted online store to buy TDS Meter for home and lab use.
1) Start with the big picture: multiple small exposures add up
Modern life brings tiny doses of pollutants from several places—water, food, air, and household products. Each source alone might look “low,” but together and over time they can stress the body, especially for children, pregnant women, elders, and people with chronic illnesses. The goal isn’t panic—it’s practical risk reduction.
2) How water gets contaminated now
a) Natural and geological sources: Some areas have naturally high salts (TDS), fluoride, arsenic, or iron in groundwater. Heavy rains can also carry soil microbes into wells.
b) Human activity:
-
- Sewage & septic leakage: Fecal bacteria, viruses, and nitrates enter surface water and borewells.
-
- Agriculture: Fertilizers (nitrates, phosphates) and pesticides run off into lakes and rivers.
-
- Industry & small workshops: Metals (lead, chromium), solvents, oils, and microplastics can reach waterways when effluent treatment is weak.
-
- Distribution system: Aging pipes add rust, biofilms, and sometimes lead from old fittings.
c) What shows up in water: Turbidity (mud), hardness (calcium/magnesium), high TDS, microbial contamination, heavy metals, pesticide traces, fluoride, nitrates, PFAS-type “forever chemicals,” and microplastics.
- Distribution system: Aging pipes add rust, biofilms, and sometimes lead from old fittings.
3) How chemicals mix with food and vegetables
a) On the farm: Pesticides, fungicides, and growth regulators may be sprayed too close to harvest, leaving residues on peels and sometimes inside produce. Irrigation with contaminated water adds microbes and heavy metals.
b) Post-harvest handling: Artificial ripening agents, waxes, dyes, and preservatives may be used improperly. Unsanitary handling spreads microbes.
c) Food processing & packaging: Additives (preservatives, colorants, flavor enhancers) are legal within limits, but misuse happens. Hot food in poor-quality plastics can leach chemicals like BPA-type substances.
d) Adulteration risks: Watered-down milk, non-permitted colors in spices, cheap oils mixed into ghee—these reduce nutrition and sometimes add toxins.
4) Chemicals commonly used at home
-
- Cleaners & disinfectants: Bleach (sodium hypochlorite), acids (toilet cleaners), ammonia, quats (benzalkonium chloride), and solvents in glass cleaners.
-
- Air fresheners & fragrances: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and phthalates can irritate lungs and trigger allergies.
-
- Pesticide sprays & coils: Pyrethroids and other insecticides help control pests but add inhalation exposure indoors.
-
- Plastic & non-stick items: Overheating poor-quality non-stick pans or microwaving in single-use plastics increases chemical migration into food.
5) Why this is dangerous for human life (the health lens)
Short-term effects: Stomach infections from microbes in water/produce; skin and eye irritation from cleaners; headaches or dizziness from solvent fumes.
Long-term risks:
-
- Metals & nitrates: Can affect blood, nerves, thyroid, and development.
-
- High fluoride: Dental or skeletal fluorosis in high-exposure regions.
-
- Persistent pollutants & microplastics: Low-dose chronic exposure is linked in research to endocrine and metabolic issues.
-
- Cumulative burden: Multiple low-level exposures can stress detox systems (liver, kidneys) over years. Vulnerable groups face higher risk at much lower doses.
6) Step-by-step: make your water safer
Test, don’t guess.
-
- Use a TDS meter to check dissolved salts.
-
- For a full picture, do a periodic lab test (microbes, nitrates, fluoride, metals). Even a basic microbiology test plus TDS is a strong start.
Step 6.2 — Choose treatment by water type.
- For a full picture, do a periodic lab test (microbes, nitrates, fluoride, metals). Even a basic microbiology test plus TDS is a strong start.
-
- Low TDS (<300 mg/L) but microbial risk: UV + UF (or boil) is usually sufficient.
-
- High TDS/hard water (>300–500 mg/L), taste issues, or metals: RO with pre-carbon + sediment filters; add UV if microbial risk exists.
-
- Visible mud/sand: Good sediment pre-filtration (5–10 micron).
Step 6.3 — Maintain the system.
- Visible mud/sand: Good sediment pre-filtration (5–10 micron).
-
- Replace sediment and carbon filters on schedule to avoid bacterial growth and bad taste.
-
- Sanitize storage tanks periodically.
-
- Check UV lamps annually; clean RO membranes as recommended.
Step 6.4 — Everyday hygiene.
- Check UV lamps annually; clean RO membranes as recommended.
-
- Store drinking water in clean, covered containers.
-
- Use separate, clean ladles; avoid dipping used glasses into storage cans.
7) Step-by-step: reduce chemicals on fruits and vegetables
Step 7.1 — Sourcing smarter.
-
- Prefer seasonal, locally grown produce; it often needs fewer preservatives and long-haul treatments.
-
- Avoid overly shiny, unnaturally uniform colors.
Step 7.2 — Washing method (simple and effective).
- Avoid overly shiny, unnaturally uniform colors.
-
- Wash hands and utensils first.
-
- Rinse produce under running water to remove dirt.
-
- Soak for 10–15 minutes in a basin with either:
-
- Clean water + a pinch of baking soda, or
-
- Clean water + a splash of edible vinegar, or
-
- Clean water + salt (mild).
-
- Soak for 10–15 minutes in a basin with either:
-
- Gently scrub firm produce (cucumbers, apples).
-
- Rinse again with clean water and air-dry.
-
- Peel when appropriate (note: peeling may reduce some nutrients but also removes surface residues).
Step 7.3 — Kitchen handling.
- Peel when appropriate (note: peeling may reduce some nutrients but also removes surface residues).
-
- Keep raw and ready-to-eat foods separate.
-
- Wash leafy layers where dust and residues hide.
-
- Don’t soak cut fruits/veg in the same water for long; rinse and use fresh water.
Step 7.4 — Cooking choices.
- Don’t soak cut fruits/veg in the same water for long; rinse and use fresh water.
-
- Blanching and cooking reduce many microbes and some residues.
-
- Avoid reheating or cooking in low-quality plastics; use glass, steel, or food-grade microwave containers.
8) Step-by-step: safer use of household chemicals
Step 8.1 — Golden “no-mix” rules.
-
- Never mix bleach with acids (like toilet cleaners) or with ammonia—this can release toxic gases.
-
- Don’t combine multiple drain cleaners or use them right after each other.
Step 8.2 — Read labels and dilute correctly.
- Don’t combine multiple drain cleaners or use them right after each other.
-
- Use the smallest effective amount. More chemical ≠ more clean.
-
- Ventilate: open windows or use exhaust during and after cleaning.
Step 8.3 — Storage & disposal.
- Ventilate: open windows or use exhaust during and after cleaning.
-
- Keep products in original labeled containers, high and locked away from children.
-
- Don’t decant cleaners into food bottles.
-
- Dispose as per local guidance—never dump concentrated chemicals into drains.
Step 8.4 — Safer swaps.
- Dispose as per local guidance—never dump concentrated chemicals into drains.
-
- For routine cleaning, warm soapy water plus microfiber often works.
-
- Spot-treat with baking soda paste (mild abrasive) or diluted vinegar on limescale (but never with bleach).
-
- Choose fragrance-free or low-VOCs products where possible.
Step 8.5 — Pest control with caution.
- Choose fragrance-free or low-VOCs products where possible.
-
- Use mechanical traps and sealing cracks first.
-
- If spraying, target nests, not the whole room; keep children and pets away; ventilate well.
9) Build a simple home exposure-reduction plan
Water: Test (TDS + microbes), pick the right purifier (RO/UV/UF), service on schedule, and store safely.
Food: Wash properly, choose seasonal, avoid heating in poor-quality plastics, and watch for suspiciously colored or overly shiny items.
Air & surfaces: Ventilate, clean dust (it can carry chemicals), and use gentler cleaners for daily tasks.
Behavior: Wash hands before eating, after handling raw foods, and after using cleaners.
10) When to seek help
-
- Sudden taste/odor/color changes in water.
-
- Cluster of stomach illnesses at home after a change in water source or filter lapse.
-
- Strong fumes, coughing, or burning eyes during cleaning—leave the area, get fresh air, and seek medical advice if symptoms persist.
-
- Local contamination news: Temporarily switch to bottled water from a reputable source and arrange lab testing.
11) Special care for vulnerable groups
-
- Infants: Use properly treated water for formula; keep bottles and nipples sterilized.
-
- Pregnant women & elders: Prioritize low-chemical cleaning options and good ventilation; avoid handling strong pesticides.
-
- People with kidney, thyroid, or immune issues: Stay consistent with water treatment and food hygiene; consult healthcare providers about local contaminants (like high fluoride or nitrates).
12) Quick checklist (print and stick on the fridge)
-
- Test water (TDS now; lab panel annually or after source changes).
-
- Right purifier for your TDS; maintain filters on time.
-
- Wash produce: rinse → soak (baking soda/vinegar/salt) → scrub/peel → final rinse.
-
- Never mix bleach with acids or ammonia.
-
- Ventilate during cleaning; use minimal effective doses.
-
- Avoid microwaving in poor-quality plastic.
-
- Prefer seasonal/local produce; be cautious of unnatural shine or color.
-
- Store chemicals safely; keep labels; don’t decant into food bottles.
-
- Keep household dust low; wash hands often.
-
- Act fast on unusual water taste/smell or strong cleaner fumes.
Bottom line: You can’t control every exposure, but you can cut most everyday risks with testing, the right water treatment, proper food washing, careful cleaner use, and good ventilation. Small, steady changes protect your family’s health—without making life complicated.
Disclaimer: This post may contains affiliate links. If you check one of them, we may receive a cute commission at no extra cost to you. Thank you.
